Herrmann Brain Dominance (HBDI)
The Herrmann Brain Dominance Instrument (or HBDI®) is a psychometric assessment that determines people's thinking preferences. The basic premise of this instrument is that it divides the brain into four quadrants: analytical, practical, relational, and experimental - each is assigned a different color. The HBDI assessment shows which combinations of quadrants individuals prefer to use while thinking. Associated reports colorfully depict style preferences, showing which style or styles are dominant. HBDI enables individuals and teams to understand and appreciate diversity of thought and communication and, as a result, achieve a better understanding of behavior leading to higher levels of performance.
Contact Lynn Reed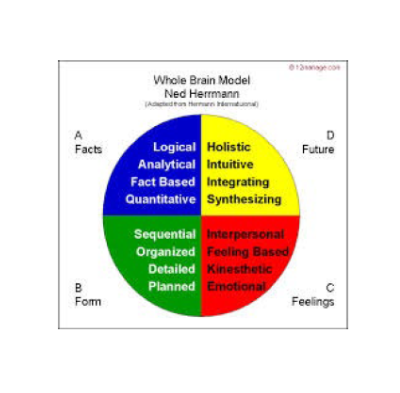
DiSC
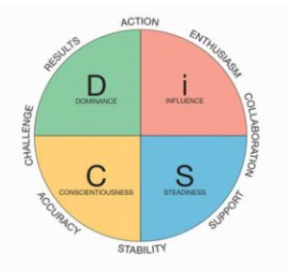
DiSC theory, researched by Dr. William Moulton Marston, is a method of identifying predictable actions and personality traits within human behavior. Marston narrowed these personality traits into four DiSC personality types: Dominance, Influence, Steadiness and Conscientiousness. The DiSC assessment measures how an individual uses a blend of these personality types to communicate, react to the environment, address conflict and much, much more. This knowledge - on both the individual and the team levels - leads to an understanding of and appreciation for personality differences, which in turn leads to a higher-performing team.
Contact Lynn ReedSocial Styles
Developed by the TRACOM Group, the social style model categorizes people according to their social styles - specifically with regard to high/low degrees of assertiveness and responsiveness. The result yields a model with four styles which are referred to as: Driver, Analytical, Amiable or Expressive, which can help people to better understand themselves and those with whom they work.
Contact Lynn Reed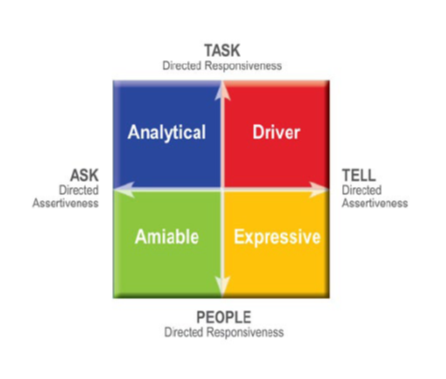

The Lencioni Pyramid
The Five Behaviors of a Cohesive Team® profile system is based on The Five Dysfunctions of a Team: A Leadership Fable by Patrick Lencioni. The assessment is based on a pyramid model of five team dysfunctions: absence of trust, fear of conflict, lack of commitment, avoidance of accountability and inattention to results. The model holds that, if a team experiences any one of these dysfunctions, then the cohesiveness of the team is in jeopardy. If, however, the behaviors of trust, conflict, commitment, accountability, and results are maximized, the team will function at the highest level possible. Each behavior in the pyramid model builds upon the previous behavior and supports the others.
Contact Lynn Reed